Page 65 - OHKF_Biotech_EN
P. 65
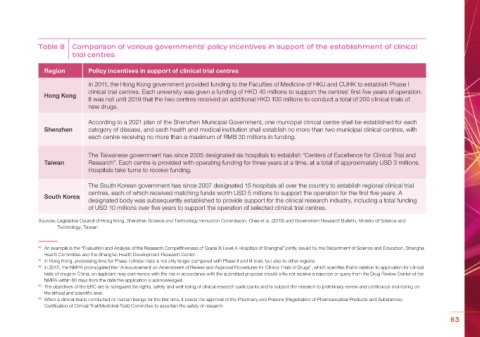
Table 8 Comparison of various governments’ policy incentives in support of the establishment of clinical
trial centres
Region Policy incentives in support of clinical trial centres
In 2011, the Hong Kong government provided funding to the Faculties of Medicine of HKU and CUHK to establish Phase I
clinical trial centres. Each university was given a funding of HKD 40 millions to support the centres’ first five years of operation.
Hong Kong
It was not until 2019 that the two centres received an additional HKD 100 millions to conduct a total of 200 clinical trials of
new drugs.
According to a 2021 plan of the Shenzhen Municipal Government, one municipal clinical centre shall be established for each
Shenzhen category of disease, and each health and medical institution shall establish no more than two municipal clinical centres, with
each centre receiving no more than a maximum of RMB 30 millions in funding.
The Taiwanese government has since 2005 designated six hospitals to establish “Centers of Excellence for Clinical Trial and
Taiwan Research”. Each centre is provided with operating funding for three years at a time, at a total of approximately USD 3 millions.
Hospitals take turns to receive funding.
The South Korean government has since 2007 designated 15 hospitals all over the country to establish regional clinical trial
centres, each of which received matching funds worth USD 5 millions to support the operation for the first five years. A
South Korea
designated body was subsequently established to provide support for the clinical research industry, including a total funding
of USD 10 millions over five years to support the operation of selected clinical trial centres.
Sources: Legislative Council of Hong Kong, Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission, Chee et al. (2016) and Government Research Bulletin, Ministry of Science and
Technology, Taiwan
60 An example is the “Evaluation and Analysis of the Research Competitiveness of Grade III Level A Hospitals of Shanghai” jointly issued by the Department of Science and Education, Shanghai
Health Committee and the Shanghai Health Development Research Center.
61 In Hong Kong, processing time for Phase I clinical trials is not only longer compared with Phase II and III trials, but also to other regions.
62 In 2015, the NMPA promulgated the “Announcement on Amendment of Review and Approval Procedures for Clinical Trials of Drugs”, which specifies that in relation to application for clinical
trials of drugs in China, an applicant may commence with the trial in accordance with the submitted proposal should s/he not receive a rejection or query from the Drug Review Center of the
NMPA within 60 days from the date the application is acknowledged.
63 The objectives of the ERC are to safeguard the rights, safety and well-being of clinical research participants and to subject the research to preliminary review and continuous monitoring on
the ethical and scientific level.
64 When a clinical trial is conducted on human beings for the first time, it needs the approval of the Pharmacy and Poisons (Registration of Pharmaceutical Products and Substances:
Certification of Clinical Trial/Medicinal Test) Committee to ascertain the safety of research.
63