Page 94 - OHKF_Gerontech_report_en
P. 94
“Don’t know”
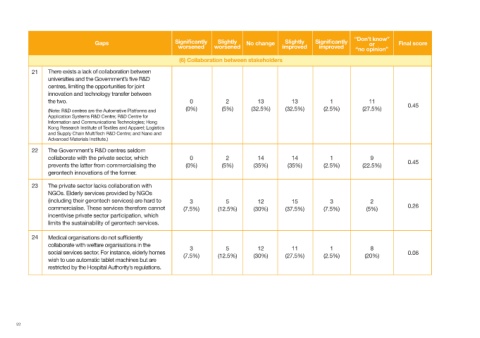
Gaps Significantly Slightly No change Slightly Significantly or Final score
worsened worsened improved improved “no opinion”
(6) Collaboration between stakeholders
21 There exists a lack of collaboration between
universities and the Government’s five R&D
centres, limiting the opportunities for joint
innovation and technology transfer between
the two. 0 2 13 13 1 11
0.45
(0%) (5%) (32.5%) (32.5%) (2.5%) (27.5%)
(Note: R&D centres are the Automative Platforms and
Application Systems R&D Centre; R&D Centre for
Information and Communications Technologies; Hong
Kong Research Institute of Textiles and Apparel; Logistics
and Supply Chain MultiTech R&D Centre; and Nano and
Advanced Materials Institute.)
22 The Government’s R&D centres seldom
collaborate with the private sector, which 0 2 14 14 1 9
0.45
prevents the latter from commercialising the (0%) (5%) (35%) (35%) (2.5%) (22.5%)
gerontech innovations of the former.
23 The private sector lacks collaboration with
NGOs. Elderly services provided by NGOs
(including their gerontech services) are hard to 3 5 12 15 3 2
commercialise. These services therefore cannot (7.5%) (12.5%) (30%) (37.5%) (7.5%) (5%) 0.26
incentivise private sector participation, which
limits the sustainability of gerontech services.
24 Medical organisations do not sufficiently
collaborate with welfare organisations in the
3 5 12 11 1 8
social services sector. For instance, elderly homes 0.06
(7.5%) (12.5%) (30%) (27.5%) (2.5%) (20%)
wish to use automatic tablet machines but are
restricted by the Hospital Authority’s regulations.
92